Introduction
In 2003 the Drug Enforcement Agency first detected levamisole in cocaine bricks. In 2008 officials in Alberta, Canada identified a cluster of unexplained cases of agranulocytosis related to cocaine contaminated with levamisole. Levamisole is a veterinary pharmaceutical used primarily to treat worm infestations in livestock. It can be easily purchased worldwide in various forms (tablets, gels, solutions, pastes and powders). Levamisole, the levo enantiomer of tetramisole, was originally developed as an antihelminthic agent. Levamisole is approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration as adjuvant chemotherapy, with 5-fluorouricil, for the treatment of colon cancer. Because it has immunostimulant and immunomodulatory properties, levamisole has also been used for treatment of various autoimmune disorders (rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, and nephrotic syndrome) and cancers (breast and lung). Levamisole is thought to increase T-cell activation and proliferation, neutrophil mobility, adherence, and chemotaxis. It is also thought to increase the formation of antibodies to various antigens. Unfortunately, it also acts as a hapten and triggers an immune reaction causing the opsonization and destruction of white blood cells.
Case presentation
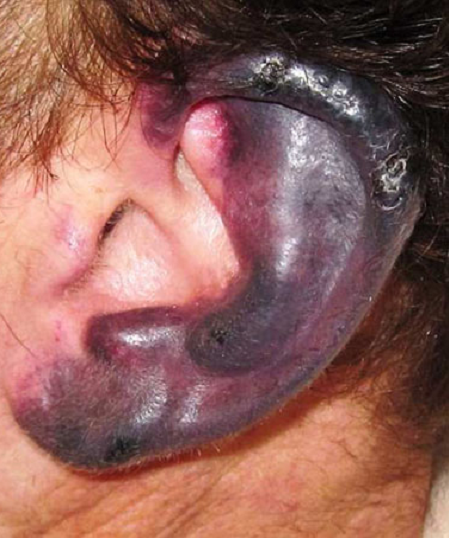
A 49 yo male presented to the emergency department for fever, chills, general malaise, weakness, and black lesions on his ears. His history was only notable for chronic cocaine use. Vital signs revealed: BP 140/90, temperature 38.7 degrees Celsius, HR 120, and Oxygen saturation of 96% on RA. He was somewhat agitated on physical exam and was noted to have necrotic lesions on both of his ears (see photo).
His laboratory tests revealed a urine toxicology immunoassay screen positive for cocaine and complete blood count demonstrating agranulocytosis 19cells/mm3. He recovered after antibiotic therapy, treatment with filgastrim (granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, G-CSF) and wound management. His crack pipe was acquired at a later time by the Drug Enforcement Agency and the remnant cocaine also tested positive for levamisole.
Questions
- What is levamisole?
- Why is levamisole is good “cutting” agent?
- What are the 3 classic clinical presentations of cocaine adulterated with levamisole?
Epidemiology
Millions people use cocaine each month in the United States. The DEA first detected levamisole in cocaine bricks in 2003. By 2008 30%-44% of cocaine exhibits were adulterated. By January 2010, per the drug intelligence brief, 73.2% of seized cocaine exhibits contained levamisole. In multiple recent studies across the country the contamination rate has varied from approximately 40% to almost 90%. Contamination has also been recently described in European countries.
Pathophysiology
A “cutting” agent is an adulterant used to increase the weight or volume of drug product and often thought to modify or increase drug effect. Addiction is complex and modulated by the dopamine and melanin-concentrating hormone systems in the mesolimbic and nucleus accumbens regions of the brain. In animal models, levamisole increases dopamine in the hypothalamus, striatum and midbrain. It is also thought to increase peripheral sympathetic activity, central neurotransmission, and form amphetamine-like metabolites. Levamisole is an excellent “cutting” agent because it is white, cheap, in powder form, easily purchased, and thought to increase the euphoric effects of cocaine. Studies have shown that there may be a genetic predisposition for the development of agranulocytosis/vasculitis in those individuals who are HLA-B27 positive or have HLA class 1 antigens. Patients may also develop antinuclear antibodies or anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies leaving them at risk. Most patients who developed agranulocytosis did so after smoking cocaine, and 50% patients had more than one episode of agranulocytosis.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is usually based upon clinical presentation and key physical examination and laboratory findings. Key laboratory tests that can be performed in the hospital setting include complete blood cell count with differential, urine toxicology screen for cocaine metabolite, bone marrow biopsy if indicated clinically as not all patients will have agranulocytosis and/or necrotic lesions simultaneously. There have also been reports of hyponatremia and acute kidney injury; therefore checking a chemistry panel in these patients is also reasonable. Levamisole can be tested for by urine and plasma GC/MS at local public health departments, reference laboratories, and crime labs, but this usually takes a few days to obtain results in most clinical settings. Urine should be positive for cocaine metabolite (benzoylecgonine).
Treatment
Guidelines for treatment are only based upon clinical experience, case series and case reports as no systematic reviews or specific therapy have been published or universally endorsed. Agranulocytosis can be halted by cessation of cocaine use, G-CSF for severe neutropenia (often not required as counts usually improve by 5-10 days), bone marrow biopsy for clinical uncertainty, and appropriate antibiotics for clinical signs of infection. Cutaneous vasculitis can be treated with cocaine cessation, antibiotics for signs of infection, possibly corticosteroids, and plastic surgery consultation if the necrosis is profound. If a patient presents with leukoencephalopathy thought to be related to cocaine contaminated with levamisole, the individual should be treated with cocaine cessation, corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), plasmapheresis, and possibly hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Discussion of case questions
- What is levamisole?
Answer: Levamisole is a veterinary pharmaceutical used primarily to treat worm infestations in livestock. It has also been used experimentally and historically to treat various autoimmune disorders and cancers in humans. Most recently it has been used as an adulterant in cocaine. - Why is levamisole is good “cutting” agent?
Answer: Levamisole is an excellent “cutting” agent because it is white, cheap, available in powder form, easily purchased, and thought to increase the euphoric effects of cocaine. - What are the 3 classic clinical presentations of levamisole?
Answer: Though few individuals will develop toxicity, physicians and poison control centers must be aware of it as an etiology for patients presenting with unexplained agranulocytosis, vasculitis, or leukoencephalopathy.



