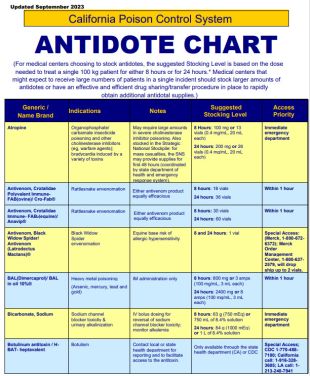
Antidote Chart
California Poison Control System | Antidote Chart click to view/print PDF
Last updated: September 2023
For medical centers choosing to stock antidotes, the suggested stocking level is based on the dose needed to treat a single 100 kg patient for 8 hours and for 24 hours.
Adapted from Dart RC, et al., Annals of Emergency Medicine, 2009; 54(3):386-394].
Medical centers that might expect to receive large numbers of patients in a single incident should stock larger amounts of antidotes or have an effective and efficient drug sharing/transfer procedure in place to rapidly obtain additional antidotal supplies.
|
Generic / Name Brand |
Indications |
Notes |
Suggested Stocking Level |
Access Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Atropine |
Organophosphate/ carbamate insecticide poisoning and other cholinesterase inhibitors (eg, warfare agents); bradycardia induced by a variety of toxins |
May require large amounts in severe cholinesterase inhibitor poisoning. Also stocked in the Strategic National Stockpile: for mass casualties, the SNS may provide supplies for first 48 hours (coordinated by state department of health and emergency response system). |
8 Hours: 100 mg or 13 vials (0.4 mg/mL, 20 mL each) 24 hours: 200 mg or 26 vials (0.4 mg/mL, 20 mL each) |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Antivenom, Crotalidae Polyvalent Immune- FAB(ovine)/ Cro-Fab® |
Rattlesnake envenomation |
Either antivenom product equally efficacious |
8 hours: 18 vials 24 hours: 36 vials |
Within 1 hour |
|
Antivenom, Crotalidae Immune- FAB2(equine)/ Anavip® |
Rattlesnake envenomation |
Either antivenom product equally efficacious |
8 hours: 30 vials 24 hours: 60 vials |
Within 1 hour |
|
Antivenom, Black Widow Spider/ Antivenom (Latrodectus Mactans)® |
Black Widow Spider envenomation |
Equine base risk of allergic hypersensitivity |
8 and 24 hours: 1 vial |
Special Access: (Merck, 1-800-672- 6372); Merck Order Management Center, 1-800-637-2579, will drop ship up to 2 vials. |
|
BAL(Dimercaprol)/ BAL in oil 10%® |
Heavy metal poisoning (Arsenic, mercury, lead and gold) |
IM administration only |
8 hours: 800 mg or 3 amps (100 mg/mL, 3 mL each) 24 hours: 2400 mg or 8 amps (100 mg/mL, 3 mL each) |
Within 1 hour |
|
Bicarbonate, Sodium |
Sodium channel blocker toxicity & urinary alkalinization |
IV bolus dosing for reversal of sodium channel blocker toxicity; monitor alkalemia |
8 hours: 63 g (750 mEq) or 750 mL of 8.4% solution 24 hours: 84 g (1000 mEq) or 1 L of 8.4% solution |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Botulinum antitoxin / H- BAT- heptavalent |
Botulism |
Contact local or state health department for reporting and to facilitate access to the antitoxin. |
Only available through the state health department (CA) or CDC |
Special Access; CDC 1-770-488- 7100; California call: 1-916-328-3605; LA call: 1-213-240-7941 |
|
Calcium Chloride injection |
Calcium channel blocker poisoning; hypocalcemia induced by various agents |
Can cause tissue necrosis if extravasation occurs – use large vein for infusion OR use calcium gluconate injection (see below) |
8 and 24 hours: 10 g or 10 vials (10%, 10 mL) |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Calcium Gluconate Powder |
Hydrofluoric acid dermal burns |
For compounding a topical gel |
8 and 24 hours: 1 x 100 g powder bottle |
Within 1 hour |
|
Hydrofluoric acid skin exposure or poisoning; hypocalcemia induced by various agents |
|
8 and 24 hours: 30 g or 30 vials (10%, 10 mL) |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Calcium Gluconate gel/ Calgonate 2.5% gel® |
Hydrofluoric acid dermal burns |
For topical burns |
8 hours: 6 x 25 g tubes 24 hours: 10 x 25 g tubes |
Within 1 hour |
|
Carnitine (L- Carnitine)/ Carnitor® |
Hyperammonemia &/or hepatotoxicity from valproic acid toxicity |
|
8 hours: 10 g or 10 x 1 g vials 24 hours: 20 g or 20 x 1 g vials |
Within 1 hour |
|
Cyanide Antidote Kit (Nithiodote by Hope Pharmaceuticals) |
Cyanide & sodium nitroprusside toxicity |
Conventional cyanide antidote: contains 1-10 mL (300 mg) vial of sodium nitrite, 1-50 mL (12.5 g) vial of sodium thiosulfate (amyl nitrite inhalant ampules not included) |
2 kits for small hospitals, 6 kits for major medical centers or stock separate supplies of sodium thiosulfate and sodium nitrite vials OR stock the Cyanokit® (hydroxocobalamin) antidote kit (see below) |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Cyanide |
Risk of methemoglobinemia and hypotension with use. |
2 x 10 mL (3%) vials; 6 vials for major medical centers |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Cyanide; sodium nitroprusside toxicity |
If used alone for cyanide toxicity, may have a slow onset of action. Thiosulfate is synergistic with sodium nitrite, and the two drugs should be used together to treat cyanide poisoning whenever possible. |
2 x 50 mL (25%) vials; 6 vials for major medical centers |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Cyanokit®/ Hydroxocobalamin |
Cyanide poisoning |
Preferred antidote for cyanide poisoning due to better safety and easier use. |
8 and 24 hours: 10 g or 2 kits |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Cyproheptadine |
Mild to moderate serotonin syndrome |
Anticholinergic side effects and only PO administration |
8 hours: 20 mg or 5 tablets (4 mg each) 24 hours: 36 mg or 9 tablets (4 mg each) |
|
|
Dantrolene |
Malignant hyperthermia |
|
8 hours: 1000 mg or 50 x 20 mg vials 24 hours: 2000 mg or 56 vials |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Deferiprone/ Ferriprox® |
Iron overload |
Oral Chelator |
8 hours: 3.3 g or 7 x 500 mg tablets 24 hours: 9.9 g or 20 x 500 mg tablets |
Specialty/optional |
|
Deferoxamine/ Desferal® |
Iron poisoning |
IV use only |
8 hours: 12 g or 6 x 2 g vials 24 hours: 36 g or 18 x 2 g vials |
Within 1 hour |
|
Digoxin Immune FAB (ovine)/ DigiFab® |
Digoxin poisoning; other cardiac glycosides (eg, oleander, foxglove) |
Consult with poison center regarding dosing, especially for cardiac glycosides other than digoxin |
8 and 24 hours: 15 vials |
Immediate emergency department |
|
DMSA (Succimer)/ Chemet® |
Heavy metal poisoning (lead, mercury, arsenic) |
|
8 hours: 1 g or 10 x 100 mg capsules 24 hours: 3 g or 30 x 100 mg capsules |
|
|
DTPA-Calcium (Diethylenetriamine pentaacetate)/ (Pentetate Calcium Trisodium injection) |
Dirty bomb agents: radioactive plutonium, americium and curium |
Only available through government sources. Stocked in the Strategic National Stockpile: supplies for first 48 hours coordinated by state department of health and emergency response system. |
8 and 24 hours: 1 x 1 g amp |
Special access - Strategic National Stockpile. The Radiation Emergency Assistance Center/Training Site (REAC/TS) can be contacted for information on use of antidote. Business hours: 1-865-576-3131; After hours: 1-865-576-1005. |
|
DTPA-Zinc (Diethylenetriamine pentaacetate)/ (Pentetate Zinc Trisodium injection) |
Dirty bomb agents: radioactive plutonium, americium and curium |
Only available through government sources. Stocked in the Strategic National Stockpile: supplies for first 48 hours coordinated by state department of health and emergency response system. |
8 and 24 hours: 1 x 1 g amp |
Special access - Strategic National Stockpile. The Radiation Emergency Assistance Center/Training Site (REAC/TS) can be contacted for information on use of antidote. Business hours: 1-865-576-3131; After hours: 1-865- 576-1005. |
|
EDTA-Calcium/ Versenate® |
Lead poisoning; also zinc, manganese, and certain radioisotopes |
Note: Do not confuse with “Sodium” EDTA |
8 hours: 1 g or 1 1000 mg/5 mL amp 24 hours: 3 g or 3 1000 mg/5 mL amps |
|
|
Ethanol IV 10% with 5% Dextrose |
Ethylene glycol or methanol poisoning |
Note: fomepizole is the preferred antidote due to easier dosing, monitoring and safety. |
8 hours: 22 x (5 mL) vials or ampules of 98% solution for injection 24 hours: 44 x (5-mL) vials or ampules (10% solution can be prepared using 98% ethanol product) |
Within 1 hour |
|
Ethanol (oral) |
Ethylene glycol or methanol poisoning |
Note: fomepizole is the preferred antidote due to easier dosing, monitoring and safety. Oral ethanol-containing beverage (eg, whiskey, vodka) can be used in an emergency situation. |
8 hours: 850 mL of 80 proof (40%) liquor 24 hours: 2450 mL of 80 proof (40%) liquor |
Within 1 hour |
|
Flumazenil |
Benzodiazepine poisoning |
Use small initial dose to avoid abrupt awakening/ delirium; use with caution in patients on chronic benzodiazepine therapy as withdrawal seizures may occur; use with caution in mixed drug overdoses. |
8 hours: 6 mg or 6 x 1 mg/10 mL vials 24 hours: 12 mg or 12 x 1 mg/10 mL vials |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Fomepizole (4-MP)/ Antizol® |
Preferred antidote for ethylene glycol or methanol poisoning |
Manufacturer of Antizol® will replace expired stocks |
8 hours: 1.5 g or 1 x 1.5 mL (1 g/mL) vials 24 hours: 4.5 g or 3 x 1.5 mL (1 g/mL) vials |
Within 1 hour |
|
Glucagon |
Beta blocker/calcium channel blocker poisoning |
Anticipate nausea and vomiting |
8 hours: 90 mg or 90 x 1 mg vials 24 hours: 250 mg or 250 x 1 mg vials |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Glucarpidase/ Voraxaze® |
Methotrexate toxic levels |
Use in patient with toxic levels and impaired renal function; glucarpidase may also metabolize leucovorin so stagger doses at least 2 hours. |
8 and 24 hours: 5 vials (1000 U/vial) |
Specialty/optional product: 1-855-786-7292 |
|
Idarucizumab/ Praxbind® |
Monoclonal antibody that binds to dabigatran and its acylglucuronide metabolites and neutralizes their anticoagulant effects |
Specific only for dabigatran; not effective for other oral anticoagulants |
8 and 24 hours: 5 g or 2 x (2.5 g/50 mL) vials |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Insulin |
Hyperinsulinemia - euglycemia (HIE) therapy for calcium antagonist and beta-blocker poisoning |
Accompany with dextrose if blood glucose < 200 mg/dL |
8 hours: 1000 U or one vial (100 U/mL, 10 mL each) 24 hours: 3000 U or three vials (100 U/mL, 10 mL each) |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Intravenous Fat Emulsion/ Intralipid® |
Lipophilic cardiotoxic drugs |
Immediately after administration several laboratory tests of patient serum/blood may be uninterpretable |
8 and 24 hours: 1500 mL of 20% or 3 bags (500 mL each) bags (500 mL each) |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Leucovorin calcium |
Folic acid antagonists / methanol |
|
8 hours: 300 mg (3 x 100 mg vials) 24 hours: 1000 mg (10 x 100 mg vials) |
Within 1 hour |
|
Methylene Blue |
Methemoglobinemia |
|
8 hours: 400 mg or 4 x 10 mL (10 mg/mL) amps 24 hours: 600 mg or 6 x 10 mL (10 mg/mL) amps |
Immediate emergency department |
|
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) Mucomyst® or generic |
Acetaminophen poisoning (oral preparation) |
Use orally. Dilute at least by a 3:1 ratio. |
8 hours: 28 g or 5 x 30 mL (20%) vials 24 hours: 56 g or 10 x 30 mL (20%) vials |
Immediate emergency department |
|
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) Acetadote® |
Acetaminophen poisoning (IV preparation) |
Note: 2 different dilutions are used (150 mg/kg/hr x 1 hour followed by 15 mg/kg/hr x 20 hours). Loading dose should be infused slowly over 60 minutes. |
8 hours: 30 g or 5 x 30 mL (20%) vials 24 hours: 54 g or 9 x 30 mL (20%) vials |
Within 1 hour |
|
Naloxone/ Narcan® |
Opioid overdose |
Use small initial dose to avoid abrupt awakening/withdrawal |
8 hours: 20 mg or 50 x 0.4 mg/2 mL amps or 2 x 10 mg/10 mL vials 24 hours: 40 mg or 4 x 10 mg/mL vials |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Octreotide acetate/ Sandostatin® |
Oral sulfonylurea poisoning and meglitinide poisoning |
Avoid long-acting depot products |
8 hours: 200 mcg or 2 x 1 mL (0.1 mg/mL) amps 24 hours: 1000 mcg or 1 x 5 mL (0.2 mg/mL) multidose vial |
Within 1 hour |
|
Physostigmine/ Antilirium® (When available) |
Anticholinergic poisoning, especially antimuscarinic delirium |
Administer at low dose (0.5 mg) and slowly, over 2-5 minutes to avoid severe adverse reactions including bradycardia, asystole and seizures (Contraindicated in TCA or similar poisoning with widened QRS intervals) |
8 and 24 hours: 4 mg or 2 x 2 mL (1 mg/mL) amps (When available) |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Potassium Iodide |
Thyroid radioiodine protection |
Highest risk groups for radioiodine-induced cancer are infants, children and pregnant and nursing females. Should only be used when directed by public health officials. |
8 and 24 hours: 130 mg |
Within 1 hour |
|
Pralidoxime(2- PAM)/ Protopam® |
Cholinesterase Inhibitor poisoning (organophosphate or “nerve gas”) |
Also stocked in the Strategic National Stockpile: for mass casualties, local cache may provide supplies for first 48 hours coordinated by state department of health and emergency response system. |
8 hours: 7 g or 7 x 1 gm (20 mL) vials 24 hours: 18 g or 18 x 1 gm (20 mL) vials |
Within 1 hour |
|
Protamine |
Heparin reversal |
May also partially neutralize low-molecular weight heparins |
8 hours: 500 mg or 2 vials (10 mg/mL, 25 mL each) 24 hours: 1250 mg or 5 vials (10 mg/mL, 25 mL each) |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Prothrombin Complex Concentrate (PCC): 3 factor and 4 factor |
Reversal of bleeding from anticoagulants (vitamin K antagonists, direct thrombin inhibitors, factor Xa inhibitors) |
Specific reversal agents may be available (idarucizumab, andexanet alpha) and Vitamin K. Otherwise, 4 factor PCC is preferred over 3 factor. Activated prothrombin complex concentrate (APCC or FEIBA) does not contain heparin and preferred for direct thrombin inhibitors. |
8 and 24 hours: 5,000 IU |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Prussian Blue/ Radiogardase® |
Dirty bomb agents: radioactive cesium and thallium and non- radioactive thallium |
Only available through government sources. Stocked in the Strategic National Stockpile: will provide supplies for first 48 hours coordinated by state department of health and emergency response system. |
8 hours: 12.5 g 24 hours: 25 g |
Special access - Strategic National Stockpile. The Radiation Emergency Assistance Center/Training Site (REAC/TS) can be contacted for information on use of antidote. Business hours: 1-865-576-3131; After hours: 1-865- 576-1005. For product acquisition contact McGuff Pharmacy: 1-877- 444-1133 |
|
Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) |
Isoniazid (INH) poisoning |
Large amounts needed for poisoning: 5 grams is the minimum antidotal dose used in an ingestion of an unknown amount. Note: the 30 mL vials may only be available from compounding pharmacies. The 100 mg in 1 mL vials may contain the preservative chlorobutanol. |
8 hours: 9 g or 3 vials (100 mg/mL, 30 mL each) or the equivalent 24 hours: 24 g or 8 vials (100 mg/mL, 30 mL each) or the equivalent (If possible: Use preservative free product or powder for reconstitution.) |
Immediate emergency department |
|
Sugammadex/ Bridion® |
Reversal of rocuronium and vecuronium (and possibly pancuronium) neuromuscular blockade. Emergent reversal dosing depends on the depth of the paralysis and can range from 2 mg/kg up to 16 mg/kg. |
This agent is used in lieu of carbamate (cholinergic) reversal agents such as neostigmine. Read more about sugammadex sodium (Rx) on Medscape. |
Available in two vial sizes: 200 mg/2 mL (100 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial for bolus injection (comes in a box of 10 vials) or 500 mg/5 mL (100 mg/mL), in a single-dose vial for bolus injection (comes in a box of 10 vials). |
Immediate-stock in areas where accidental administration of paralytics may occur (Emergency Department of Operating Room) |
|
Uridine triacetate/ Vistogard® |
5-FU, capecitabine poisoning |
Recommended for use within 96 hours of last dose where toxicity is evident or expected; doses of up to 10 grams every 6 hours for a total of 20 doses have been well-tolerated. |
8 hours: 20 g or 2 x 10 g packets 24 hours: 40 g or 4 x 10 g packets |
Wellstat Medical: 1- 800-914-0071 or Cardinal Health Specialty: 1- 866-677-4844 |
|
Vitamin K1(Phytonadione)/ Mephyton® or AquaMephyton® |
Warfarin, warfarin-based anticoagulants and super-warfarin based rodenticide poisoning |
If patient is actively bleeding use fresh frozen plasma or Factor VII concentrate or prothrombin complex concentrates. |
8 hours: 50 mg or 10 x 5 mg tabs or 5 x 10 mg/mL amps 24 hours: 100 mg or 40 x 5 mg tabs or 20 x 10 mg/mL amps |
Immediate emergency department |
Note: List is not all-inclusive but reflects agents used more exclusively as antidotes or antidotal agents used infrequently.